What is Data Structure? And What are the types of Data Structure?
What are Data Structures?
Data structure is a storage that is
used to store and organize data in a particular manner. It is a way of
arranging data on a computer so that it can be accessed and updated efficiently.
According to your project
requirements, it is important to choose the right data structure for your
project.
For example:- if you want to store data sequentially in the memory, then you can go for the Array data structure.
Fig. 1 (type of data structure)
Types of Data Structure
Basically,
data structures are divided into two categories:
1. Linear
data structure
2. Non-linear
data structure
Linear data structures
In linear data structures, the elements are arranged in sequence one after the other. Since elements are arranged in a particular order, they are easy to implement.
However, when the complexity of the program increases, the linear data structures might not be the best choice because of operational complexities.
Popular linear data structures are:
1. Array Data Structure
In an array, elements in memory are arranged in continuous memory. All the elements of an array are of the same type. And, the type of elements that can be stored in the form of arrays is determined by the programming language.
Ø An array with each element represented by
an index
Fig. 2 (Array data structure)
2. Stack Data Structure
In the stack data structure, elements are stored in the LIFO (last in first out) principle. That is, the last element stored in a stack will be removed first from the stack and the first element stored in a stack will be removed last from the stack.
Example: - It works just like a pile of plates where the last plate kept on the pile will be removed first. To learn more, visit
Ø In a stack, an operation can be performed only
from one end (top of the stack)
 Fig. 3 (Stack data structure)
Fig. 3 (Stack data structure)

3. Queue Data Structure
Unlike stack, the queue data structure works in the FIFO (first in first out) principle where the first element stored in the queue will be removed first and then second, third, and so on.
It works just like a queue of people at the ticket counter where the first person in the queue will get the ticket first and then second, third, and so on.
Ø In a queue, addition and removal
are performed from separate ends.
Fig. 4 (Queue data structure)
4. Linked List Data
Structure
In a linked list data structure, data
elements are connected through a series of nodes. And, each node contains the
data items and addresses to the next node.
Fig. 4 (Link list data structure)
Non-linear data structures:-
Unlike linear data structures, elements in non-linear data structures are not in any sequence. Instead, they are arranged in a hierarchical manner where one element will be connected to one or more elements.
Non-linear data structures are further divided into graph and tree-based data structures.
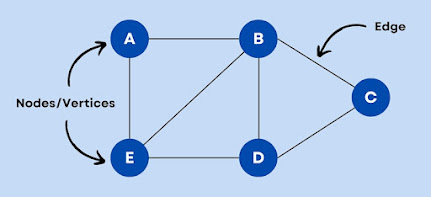
1. Graph Data Structure
In graph data structure, each node is called vertex and each
vertex is connected to other vertices through edges.
Fig. 5 (Graph data structure)
Popular Graph-Based Data Structures:
· Spanning Tree and Minimum Spanning Tree
2. Trees Data Structure
Similar to a graph, a tree is also a collection of vertices and edges. However, in the tree data structure, there can only be one edge between two vertices.
fig.6 (Tree data structure)
Popular Tree-based Data Structure:-
· AVL Tree
· B-Tree
· B+ Tree










Post a Comment